Internals and Architecture
Get to know the SQreamDB key functions and system architecture components, best practices, customization possibilities, and optimizations.
SQreamDB leverages GPU acceleration as an essential component of its core database operations, significantly enhancing columnar data processing. This integral GPU utilization isn’t an optional feature but is fundamental to a wide range of data tasks such as GROUP BY, scalar functions, JOIN, ORDER BY, and more. This approach harnesses the inherent parallelism of GPUs, effectively employing a single instruction to process multiple values, akin to the Single-Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) concept, tailored for high-throughput operations.
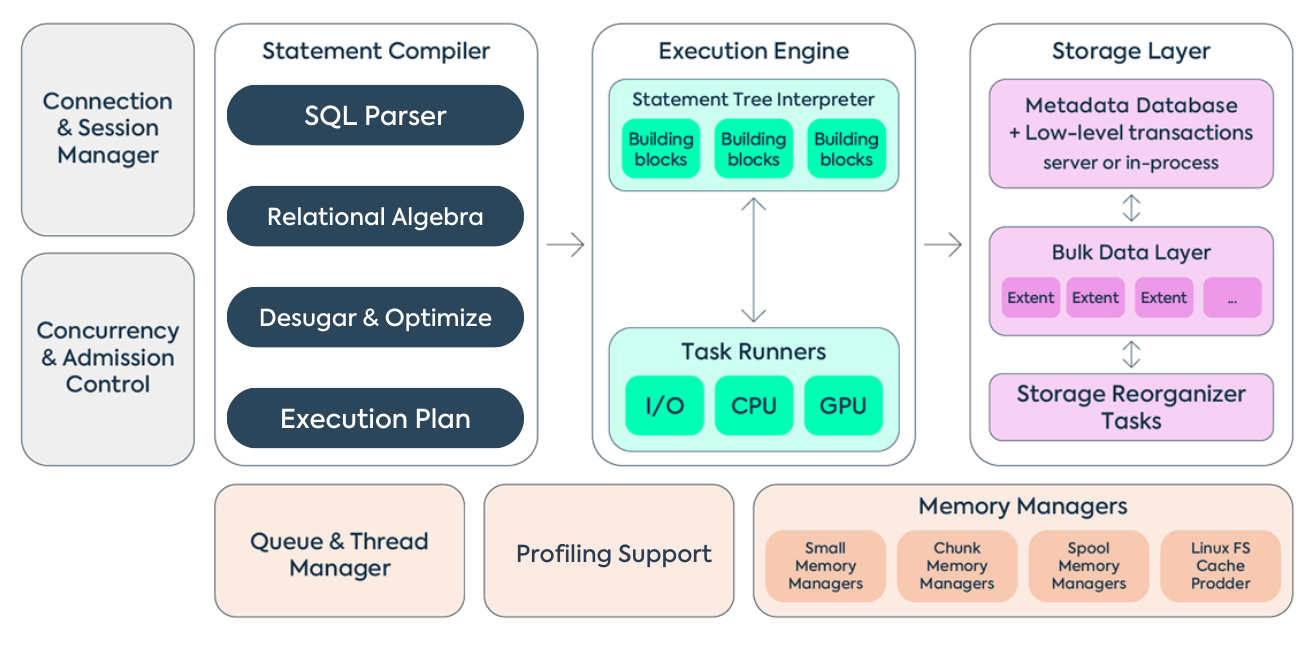
Concurrency and Admission Control
The SQreamDB execution engine employs thread workers and message passing for its foundation. This threading approach enables the concurrent execution of diverse operations, seamlessly integrating IO and GPU tasks with CPU operations while boosting the performance of CPU-intensive tasks.
Learn more about Concurrency and Scaling in SQream DB.
Statement Compiler
The Statement Compiler, developed using Haskell, accepts SQL text and generates optimized statement execution plans.
Building Blocks (GPU Workers)
In SQreamDB, the main workload is carried out by specialized C++/CUDA building blocks, also known as Workers, which intentionally lack inherent intelligence and require precise instructions for operation. Effectively assembling these components relies largely on the capabilities of the statement compiler.
Storage Layer
The storage is split into the metadata layer and an append-only data layer.
Metadata Layer
Utilizing RocksDB key/value data store, the metadata layer incorporates features such as snapshots and atomic writes within the transaction system, while working in conjunction with the append-only bulk data layer to maintain overall data consistency.
Bulk Data Layer Optimization
SQreamDB harnesses the power of its columnar storage architecture within the bulk data layer for performance optimization. This layer employs IO-optimized extents containing compression-enabled CPU and GPU-efficient chunks. Even during small insert operations, SQreamDB maintains efficiency by generating less optimized chunks and extents as needed. This is achieved through background transactional reorganization, such as DeferredGather, that doesn’t disrupt Data Manipulation Language (DML) operations. Deferred Gather optimizes GPU processing by selectively gathering only the necessary columns after GPU execution, effectively conserving memory and enhancing query performance.
The system initially writes small chunks via small inserts and subsequently reorganizes them, facilitating swift medium-sized insert transactions and rapid queries. This optimization strategy, coupled with SQreamDB’s columnar storage, ensures peak performance across diverse data processing tasks.
Transactions
SQreamDB has serializable (auto commit) transactions, with these features:
Serializable, with any kind of statement
Run multiple SELECT queries concurrently with anything
Run multiple inserts to the same table at the same time
Cannot run multiple statements in a single transaction
Other operations such as DELETE, TRUNCATE, and DDL use coarse-grained exclusive locking.