DELETE
Overview
The DELETE statement is used to remove specific rows from a table.
SQream deletes data in the following steps:
The designated rows are marked as deleted, but remain on-disk until the user initiates a clean-up process.
The user initiates a clean-up process is initiated to delete the rows.
For more information about SQream’s delete methodology, see the Deleting Data guide.
Note the following:
The ALTER TABLE and other DDL operations are blocked on tables that require clean-up.
The value expression for deletion cannot be the result of a sub-query or join.
SQream may abort delete processes exceeding a pre-defined time threshold. If the estimated time exceeds the threshold, an error message is displayed with an description for overriding the threshold and continuing with the delete.
For more information about SQream’s delete methodology, see the Deleting Data guide.
Tip
To delete all rows from a table, see TRUNCATE
To delete columns, see DROP COLUMN.
Permissions
To execute the DELETE statement, the DELETE and SELECT permissions must be assigned to the role at the table level.
For more information about assigning permissions to roles, see Creating, Assigning, and Managing Roles and Permissions.
Syntax
The following is the correct syntax for executing the DELETE statement:
delete_table_statement ::=
DELETE FROM [schema_name.]table_name [ WHERE value_expr ]
;
table_name ::= identifier
schema_name ::= identifier
The following is the correct syntax for triggering a clean-up:
chunk_cleanup_statement ::=
SELECT CLEANUP_CHUNKS ( 'schema_name', 'table_name' )
;
extent_cleanup_statement ::=
SELECT CLEANUP_EXTENTS ( 'schema_name', 'table_name' )
;
table_name ::= identifier
schema_name ::= identifier
For systems with delete parallelism capabilities, use the following syntax to enhance deletion performance and shorten runtime:
SELECT set_parallel_delete_threads(x);
Note
You may configure up to 10 threads.
Parameters
The following table describes the parameters used for executing the DELETE statement:
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
The name of the schema for the table. |
|
The name of the table to delete rows from. |
|
An expression that returns Boolean values using columns, such as |
Examples
The Examples section shows the following examples:
Deleting Values from a Table
The following shows an example of deleting values from a table:
farm=> SELECT * FROM cool_animals;
1,Dog ,7
2,Possum ,3
3,Cat ,5
4,Elephant ,6500
5,Rhinoceros ,2100
6,\N,\N
6 rows
farm=> DELETE FROM cool_animals WHERE weight > 1000;
executed
farm=> SELECT * FROM cool_animals;
1,Dog ,7
2,Possum ,3
3,Cat ,5
6,\N,\N
4 rows
Deleting Values Based on More Complex Predicates
The following shows an example of deleting values based on more complex predicates:
farm=> SELECT * FROM cool_animals;
1,Dog ,7
2,Possum ,3
3,Cat ,5
4,Elephant ,6500
5,Rhinoceros ,2100
6,\N,\N
6 rows
farm=> DELETE FROM cool_animals WHERE weight > 1000;
executed
farm=> SELECT * FROM cool_animals;
1,Dog ,7
2,Possum ,3
3,Cat ,5
6,\N,\N
4 rows
Deleting Values that Contain Multi-Table Conditions
The following shows an example of deleting values that contain multi-table conditions. The example is based on the following tables:
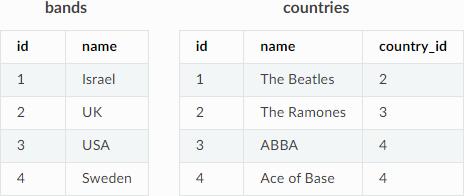
The statement below uses the EXISTS subquery to delete all bands based in Sweden:
DELETE FROM bands
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT 1 FROM countries
WHERE countries.country_id=bands.id
AND country.name = 'Sweden'
);
Identifying and Cleaning Up Tables
The following section shows examples of each phase required for cleaning up tables:
Listing Tables that Require Clean-Up
The following shows an example of listing tables that require clean-up:
farm=> SELECT t.table_name FROM sqream_catalog.delete_predicates dp
JOIN sqream_catalog.tables t
ON dp.table_id = t.table_id
GROUP BY 1;
cool_animals
1 row
Identify Clean-Up Predicates
The following shows an example of listing the clean-up predicates:
farm=> SELECT delete_predicate FROM sqream_catalog.delete_predicates dp
JOIN sqream_catalog.tables t
ON dp.table_id = t.table_id
WHERE t.table_name = 'cool_animals';
weight > 1000
1 row
Triggering a Clean-Up
The following shows an example of triggering a clean-up:
-- Chunk reorganization (SWEEP)
farm=> SELECT CLEANUP_CHUNKS('public','cool_animals');
executed
-- Delete leftover files (VACUUM)
farm=> SELECT CLEANUP_EXTENTS('public','cool_animals');
executed
farm=> SELECT delete_predicate FROM sqream_catalog.delete_predicates dp
JOIN sqream_catalog.tables t
ON dp.table_id = t.table_id
WHERE t.table_name = 'cool_animals';
0 rows